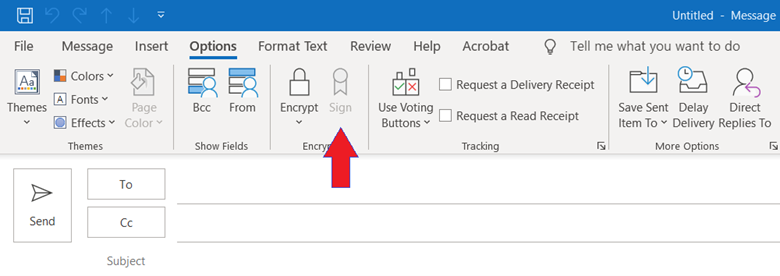
Over the next few weeks Coast Guard users will notice that all outgoing email messages will have digital signatures enabled by default. You can see this by navigating to the “Options” menu while composing an email and looking at the “Sign” option.
The option to remove the digital signature will not be available. This change will not impact Outlook Webmail or Mobility devices.
What is a Digital signature?
A digital signature is a type of electronic signature – a mathematical algorithm, actually – that guarantees the integrity of a message. It’s basically proof that you (the sender) are who you say you are. It also confirms that you created the information in the message and that it hasn’t been altered.
If you are experiencing issues with digital signatures, please refer to the following guide.
Why do I need a digital signature on my messages?
The Department of Defense now requires that all outgoing messages have digital signature enabled by default. Since Coast Guard networks are within the boundaries of the Department of Defense Information Network (DoDIN), we are required to follow DoD cybersecurity measures.
In addition, Coast Guard cybersecurity policy mandates a digital signature on all emails sent to recipients external of the .mil, .dhs, .gov domains and any email with sensitive data sent within these domains. This is an important cybersecurity measure that protects Coast Guard information and guarantees the integrity of the message.
How does a digital signature work?
When you send an email, a hash (called a message digest) is created of the message and encrypted using the sender’s private key. Upon receipt, the recipient creates a hash of the message and then uses the senders public key to decrypt the message digest and the client compares the two hashes. This confirms both the authenticity of the sender and the integrity of the message.
You can find out more about digital signatures from the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) here.
Resources:
In the news: